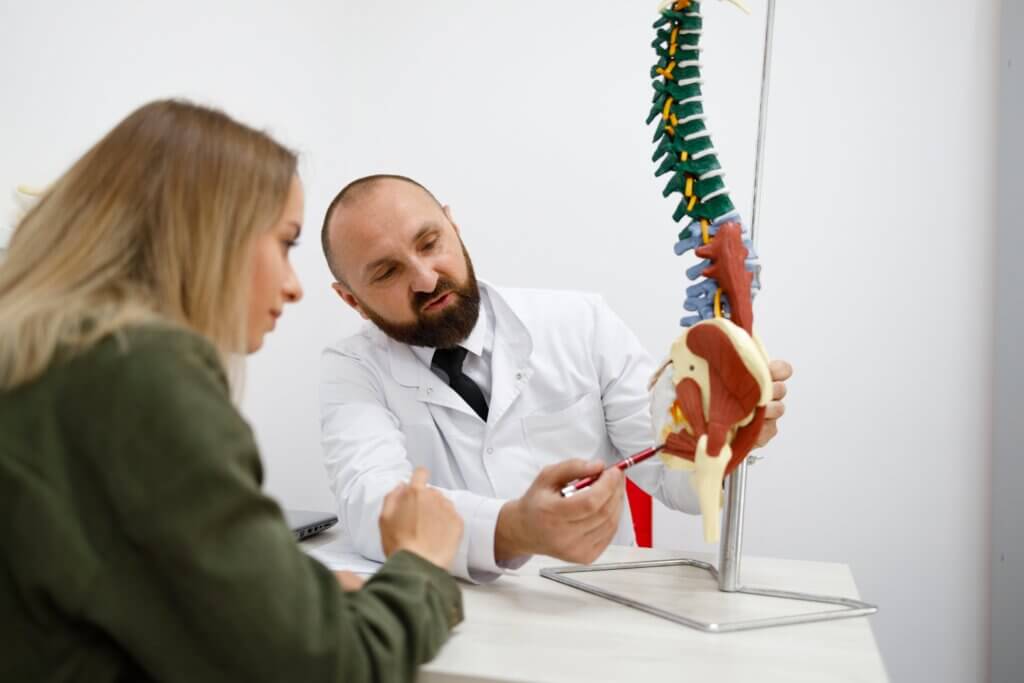
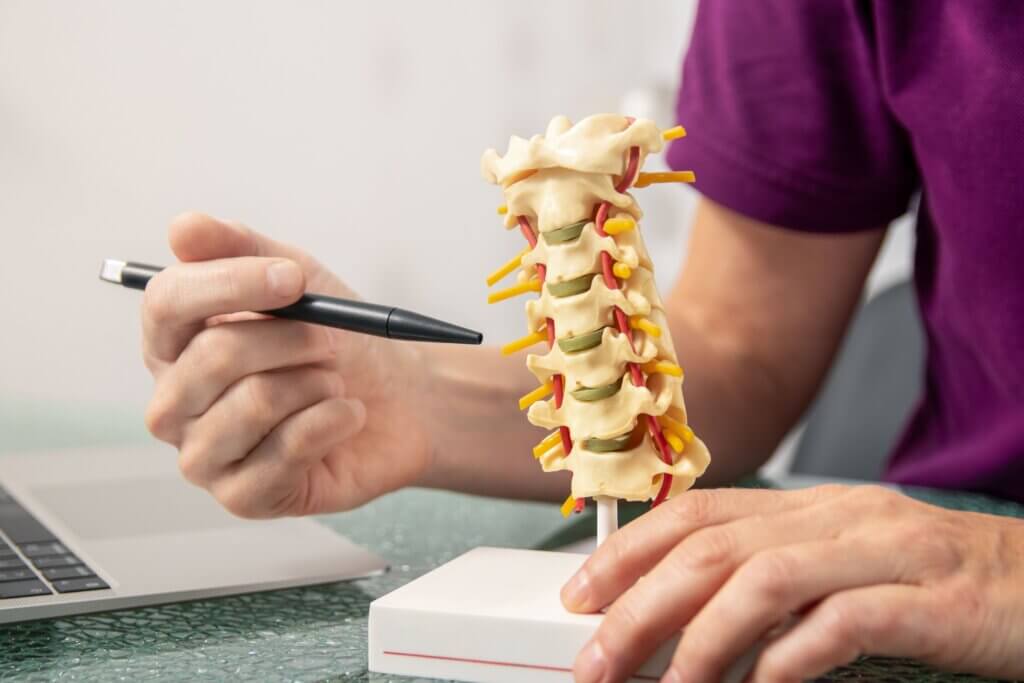
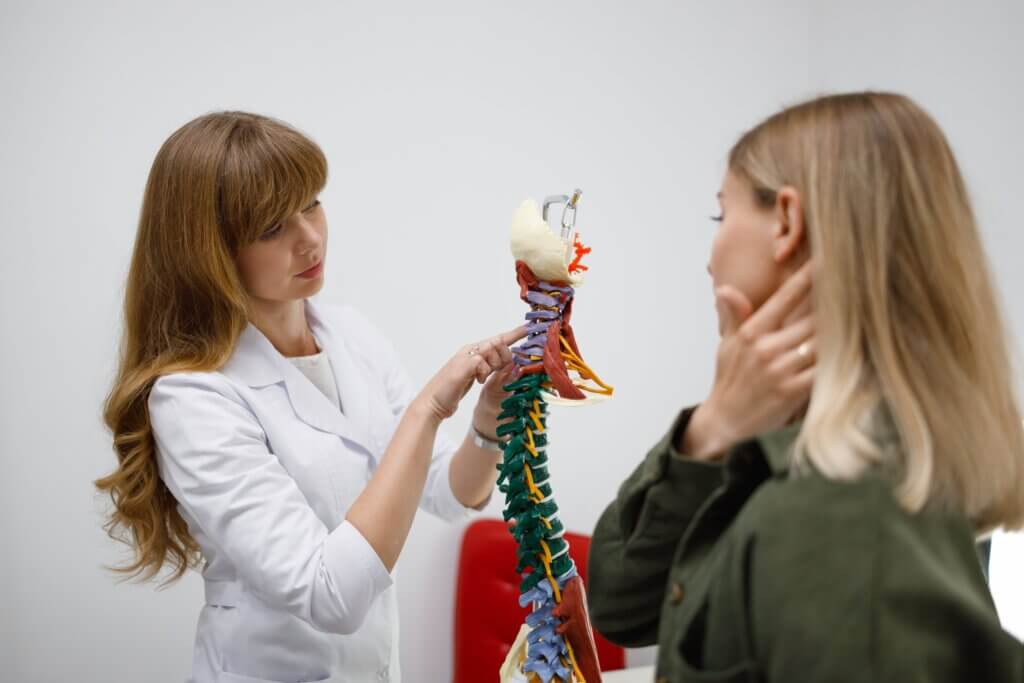
Pinched Nerve vs Herniated Disc Term What It Means Pinched Nerve A nerve is compressed or irritated by surrounding structures—can be due to a herniated disc, bone spur, tight muscles, or inflammation. Herniated Disc A disc has torn, and its inner gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) pushes out, possibly pressing on a nearby nerve. Term What It Means Pinched Nerve A nerve is compressed or irritated by surrounding structures—can be due to a herniated disc, bone spur, tight muscles, or inflammation. Herniated Disc A disc has torn, and its inner gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) pushes out, possibly pressing on a nearby nerve. Feature Pinched Nerve Herniated Disc Pain Sharp, shooting pain along nerve (e.g., sciatica) Local + radiating pain (if pressing on nerve) Numbness/tingling Yes – in nerve distribution (leg or arm) Yes – common if nerve is affected Weakness Possible Yes, if motor nerve roots involved Location Anywhere nerve gets compressed Most common at L4-L5, L5-S1, C5-C6, C6-C7 Pinched Nerve Herniated Disc Rest, NSAIDs, stretching Conservative care first (PT, meds) Nerve glides, decompression therapy Epidural injections if nerve irritation persists Surgery if severe or not improving Microdiscectomy, disc replacement, or laminectomy possible